Explore our archives database and discover more than 8,000 years of history.
The Madain Project is a very unique resource for the study of history and archaeology of three major Abrahamic Faiths. The Madain Project presents the material evidence without the influence of the religious beliefs.
An extensive index of terms, names, places, people and artefacts.
Explore Our Glossary
The Barbar Temple (معبد باربار) is an ancient archaeological site belonging to the Bronze Age Dilmun culture, located in the village of Barbar, Bahrain. The site is the location of at least three known temple structures, built successively over each other during a period of some six hundred to eight hundred years. Explore Bronze Age Barbar Temple of Dilmun

The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient hill-top citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the historic city of Athens and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historic significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. During ancient times it was known also more properly as Cecropia, after the legendary serpent-man, Cecrops. Explore Athens Acropolis
This book is a magnificent excursion led by R. A. Schwaller de Lubicz to the monuments, ruins, statues, and bas-reliefs of the temples of Karnak. With nearly 600 photographs by Georges and Valentine de Mire, more than 450 of which are full-page plates, this volume is the only complete photographic record of this important historic site.
See on Amazon
Civilization was born eight thousand years ago, between the floodplains of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, when migrants from the surrounding mountains and deserts began to create increasingly sophisticated urban societies. In the cities that they built, half of human history took place.
See on Amazon
Venerated for millennia by three faiths, torn by irreconcilable conflict, conquered, rebuilt, and mourned for again and again, Jerusalem is a sacred city whose very sacredness has engendered terrible tragedy. In this fascinating volume, Karen Armstrong, author of the highly praised A History of God, traces the history of how Jews, Christians, and Muslims have all laid claim to Jerusalem.
See on Amazon
This exceptional read written by Eckart Frahm who is professor of Assyriology in the department of Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations at Yale. At its height in 660 BCE, the kingdom of Assyria stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf. It was the first empire the world had ever seen. Here, historian Eckart Frahm tells the epic story of Assyria and its formative role in global history.
See on Amazon


Dating to the Bronze Age, it served as a multifunctional complex that combined administrative, religious, and residential functions. It is intricately linked to Greek mythology, particularly the legend of the Minotaur and the Labyrinth, enhancing its historical and cultural significance.
Explore the Minoan Palace
The 'Aurochs of Qurta' or the Qurta Inscriptions or petroglyphs are a set of stone-carvings of aurochs and stylized humans dating back to the Late Palaeolithic (circa 23,000-11,000 years ago). The rock art sites are situated near the modern village of Qurta, on the east bank of the river Nile.
Aurochs of Qurta
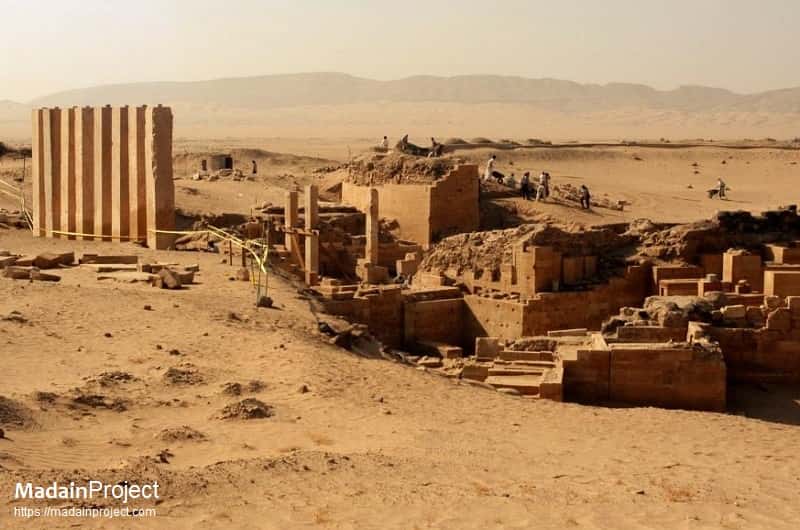

The Temple of Awwam, also spelled Awam, (معبد اوام) or "Mahram Bilqis" is a Sabaean temple dedicated to the principal deity of Saba, Almaqah, near Ma'rib in what is now modern day Yemen. It was made about the time of the emergence of Sabaean culture.
Explore Awwam Temple
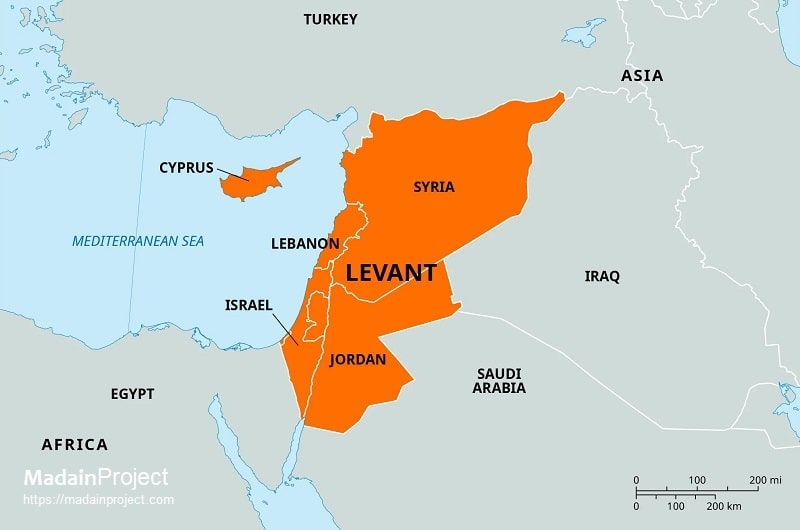
The Levant is a historical and geographical term referring to the easternmost region of the Mediterranean, encompassing lands where Europe, Asia, and Africa converge. In its broadest sense, it signifies the coastal and hinterland zones.
Explore Levant
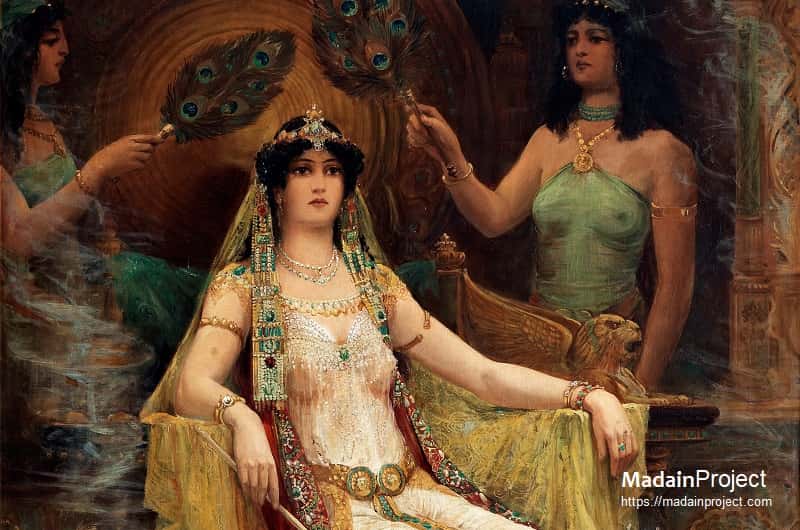

The Queen of Sheba refers to a female sovereign mentioned in multiple ancient literary traditions—Hebrew, Christian, Islamic, and Ethiopian—who is associated with the kingdom of Sheba (identified with modern day Ma'arib), a wealthy polity located either in southern Arabia (modern-day Yemen) or the Horn of Africa.
Queen of Sheba

Ancient Hattusa (also Ḫattuša or Hattusas) was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Türkiye, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River (Hittite: Marashantiya; Greek: Halys). It served as the political, administrative, and religious center of the Hittites.
Explore Ancient Hattusa

Ancient Arabia refers to the historical period before the rise of Islam in the 7th century CE. It was a region characterized by a diverse array of tribes, cultures, and civilizations. The earliest sedentary culture in Saudi Arabia dates back to the Ubaid period when Paleolithic era when nomadic hunter-gatherers roamed its arid landscapes.
Explore Ancient Arabia

The Forma Urbis Romae, also known as the Severan Marble Plan, was a massive marble map of ancient Rome, believed to have been created during the reign of emperor Septimius Severus between 203 and 211 CE. The map depicted every architectural feature in the city, ranging from grand imperial monuments to houses of the poor.
Explore Ancient Forma Urbis Romae
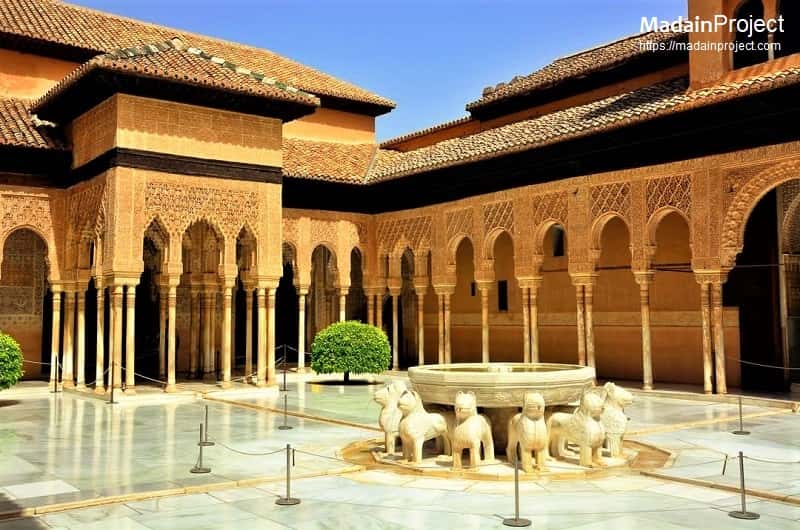

The Court of the Lions is the main courtyard of the Nasrid dynasty Palace of the Lions in the heart of the Alhambra, the Moorish citadel formed by a complex of palaces, gardens and forts in Granada, Spain. The Palace of the Lions was the architectural pinnacle of the Alhambra. The site is now part of the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Explore Court of the Lions

The Archaic Period is a term used in archaeology and historical scholarship to define an early formative phase of a civilization. It marks a stage which include the formation of urban centers, emergence of early writing systems, centralization of authority, and the development of formal artistic and religious traditions.
Explore Archaic Period
Theban Mapping Project
There is evidence of human activity in northeastern Africa since the Middle Pleistocene Period. By the Middle and Upper Paleolithic, between 90,000 to 10,000 years ago, there was a gradual movement of hunter-gatherer populations into the prehistoric Nile Valley and the drying lake and savannah regions of the Eastern Sahara precipitated by climatic changes. Traces of these early peoples survive in the forms of stone tools and rock carvings on the higher terraces along the Nile (including the western Theban plateau) and in the oases. As the nomadic hunter-gatherers came to settle along the edges of the Nile Valley, a transition to a settled lifestyle dependent on agriculture took place.
See the Entire Timeline
Explore Theban Mapping Project
Ancient Egypt
In the ancient burial ground at Saqqara, Egypt, one animal cemetery alone has yielded over four million individual ibis mummies. And the nearby dog cemetery contained over seven million mummies, with countless others found throughout Egypt.
Watch on Youtube / Explore Ancient Egypt
al Khazneh (الخزنة) was originally built as a mausoleum and crypt at the beginning of the 1st century CE during the reign of Aretas IV Philopatris. Its Arabic name Treasury derives from one legend that bandits or pirates hid their loot in a stone urn high on the second level.
Watch on Youtube / Explore al-Khazneh
The Castel Sant'Angelo, meaning the "Castle of the Holy Angel", is a massive cylindrical building located in Rome, Italy. It was originally built as a mausoleum for the Roman Emperor Hadrian in the second century CE, and later served as a fortress and castle from the fifth century onwards.
Watch on Youtube / Explore Castel Sant'Angelo
Who built the first Ishtar Gate?
The ishtar gate was constructed during the reign of King Nebuchadnezzar II in the sixth century BCE. Adorned with vibrant blue-glazed tiles depicting awe-inspiring dragons and divine beings, the Ishtar Gate served as the southern entrance to the ancient city of Babylon, acting as both a symbol of the city's power and a magnificent homage to the goddess Ishtar, the Babylonian deity of love and war.
The gate itself served as the northern entrance to Babylon and was dedicated to the Babylonian goddess Ishtar, the deity of love, fertility, and war. It was not just a functional gateway but also a symbolic passage into the heart of Babylon, meant to awe and inspire all who entered.
Signup for our monthly newsletter / online magazine.
No spam, we promise.
